Deploy Velero for backup and restore in a Tanzu Community Edition (TCE) cluster

Update 2022-10-21: After just one year in the wild VMware announced on Oct 21 2022 that they would no longer update or maintain the TCE project and that by end of 2022 the Github project will be removed. For more information check out my blog post here
Most of the things mentioned in this post (outside of installing TCE) should still be valid for other Kubernetes distributions
I've previously written about how to set up Velero for Backup/Restore functionality in a Tanzu Kubernetes Cluster.
In this post we'll see how we can do the same in a Tanzu Community Edition (TCE) cluster, but this time we'll deploy Velero from the Tanzu Package repository. As disussed in the previous post Velero in this setup will only backup resources running in the Kubernetes cluster, not the infrastructure behind it.
2022-01-27: Please be aware that the Velero website has some issues so the links to the official documentation in this blog post might not work. To workaround substitue velero.io with velero.netlify.app
I'll use the same MinIO object storage server as I did in the previous post, but the target will be a different bucket
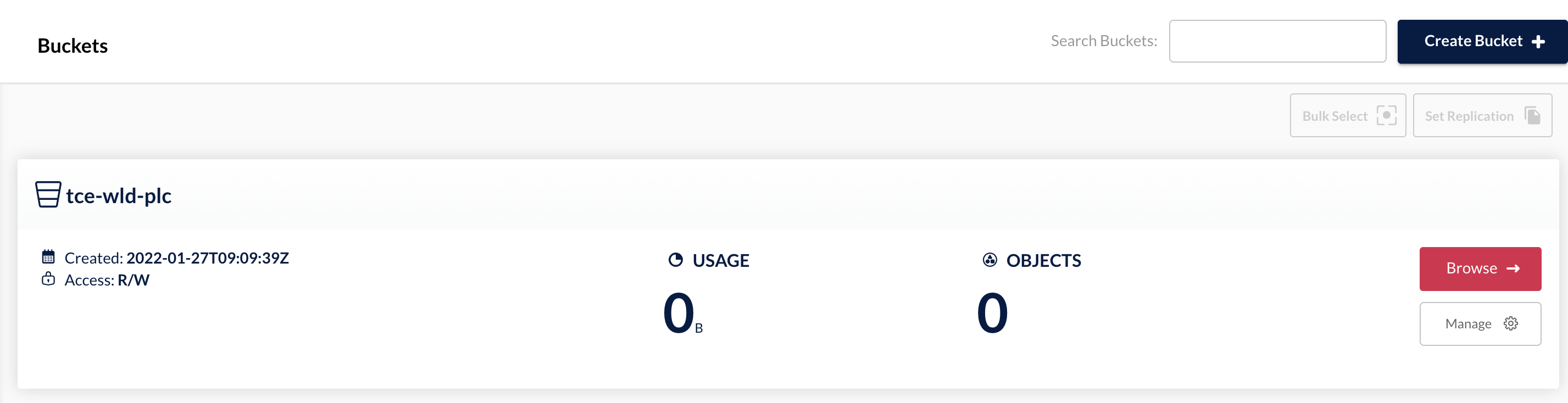
Note that MinIO isn't directly supported as a provider, but since it supports the same S3 API used in AWS we can use AWS as our provider
Tanzu Package config
The Velero package can be found in the Tanzu Package Repository and the documentation explains the available configuration parameters and how to configure against AWS and Azure. Be sure to check out the actual values from the package it self as well, as I've found that there are a few parameters not discussed in the documentation.
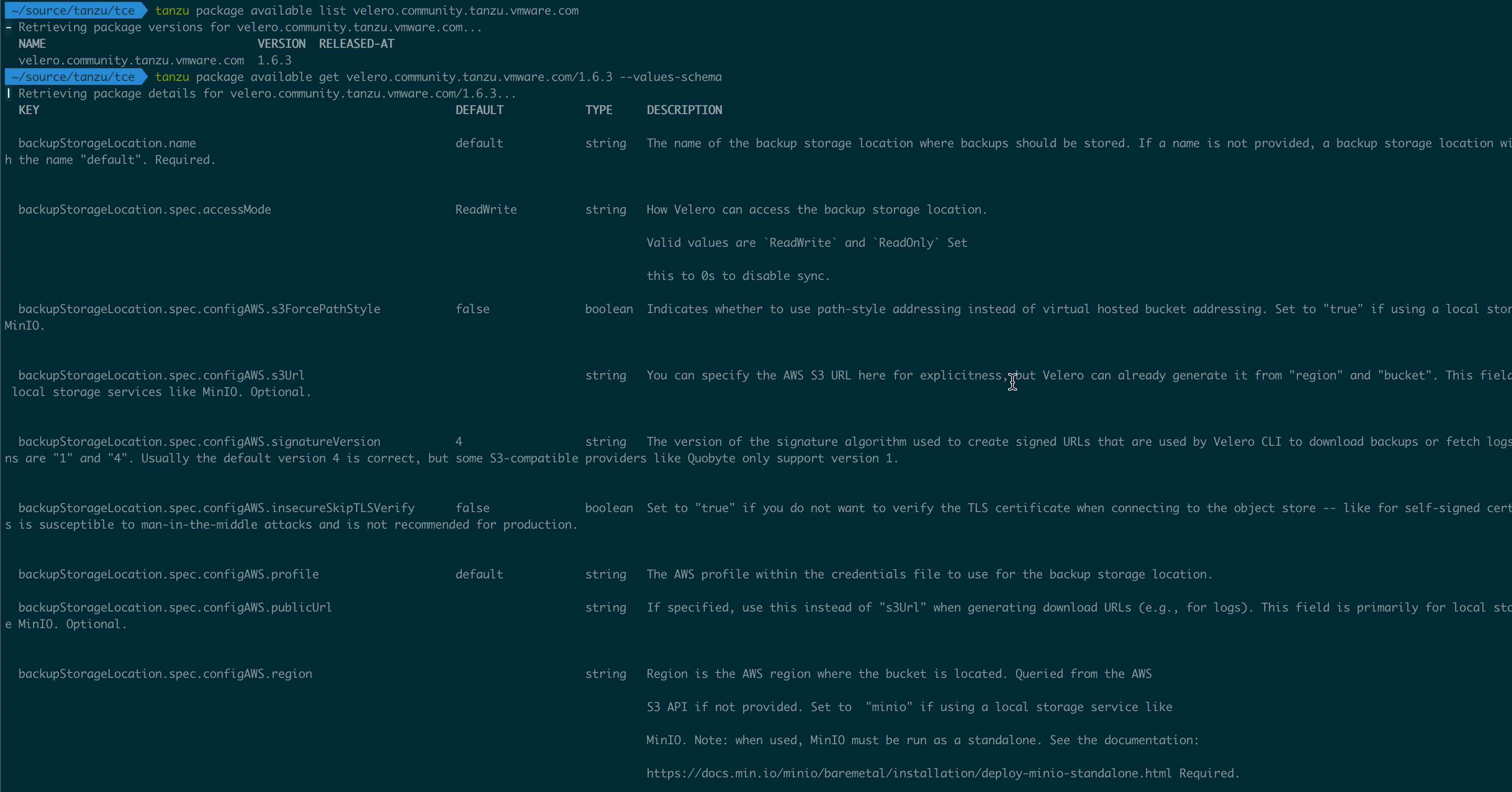
Over in MinIO I've created credentials to use in form of an access_key with a corresponding secret_access_key. We can pre-create this in our Kubernetes cluster (see my previous post), or specify it directly in the package config file. For the sake of this demo I'll specify it directly in the config file.
We also have to specify the provider, aws in my case, and which bucket to use. There's also settings for prefixing etc, refer to the documentation for that (be sure to check out the values-schema from the repository as well as the Tanzu documentation)
One important thing to configure is the region in case of the aws provider. In my case I've also set the publicUrl and s3Url to my MinIO server since I'm using that instead of public AWS and I've set the s3ForcePathStyle to true
In this demo I'm not going to use the volume snapshot functionality so I've disabled that
Note that even though I've disabled the snapshot functionality the deployment failed with the following error
fail: a region must be set for the AWS volume snapshot location. I got around this by adding a region to the spec even though I've selected to disable the feature
1namespace: velero
2credential:
3 useDefaultSecret: true
4 name: cloud-credentials
5 secretContents:
6 cloud: |
7 [default]
8 aws_access_key_id=<access_key>
9 aws_secret_access_key=<secret_key>
10backupStorageLocation:
11 name: <name>
12 spec:
13 provider: aws
14 default: true
15 objectStorage:
16 bucket: <bucket-name>
17 configAWS:
18 region: minio
19 s3ForcePathStyle: "true"
20 publicUrl: <url-to-provider>
21 s3Url: <url-to-provider>
22volumeSnapshotLocation:
23 snapshotEnabled: false
24 spec:
25 configAWS:
26 region: us-east-1
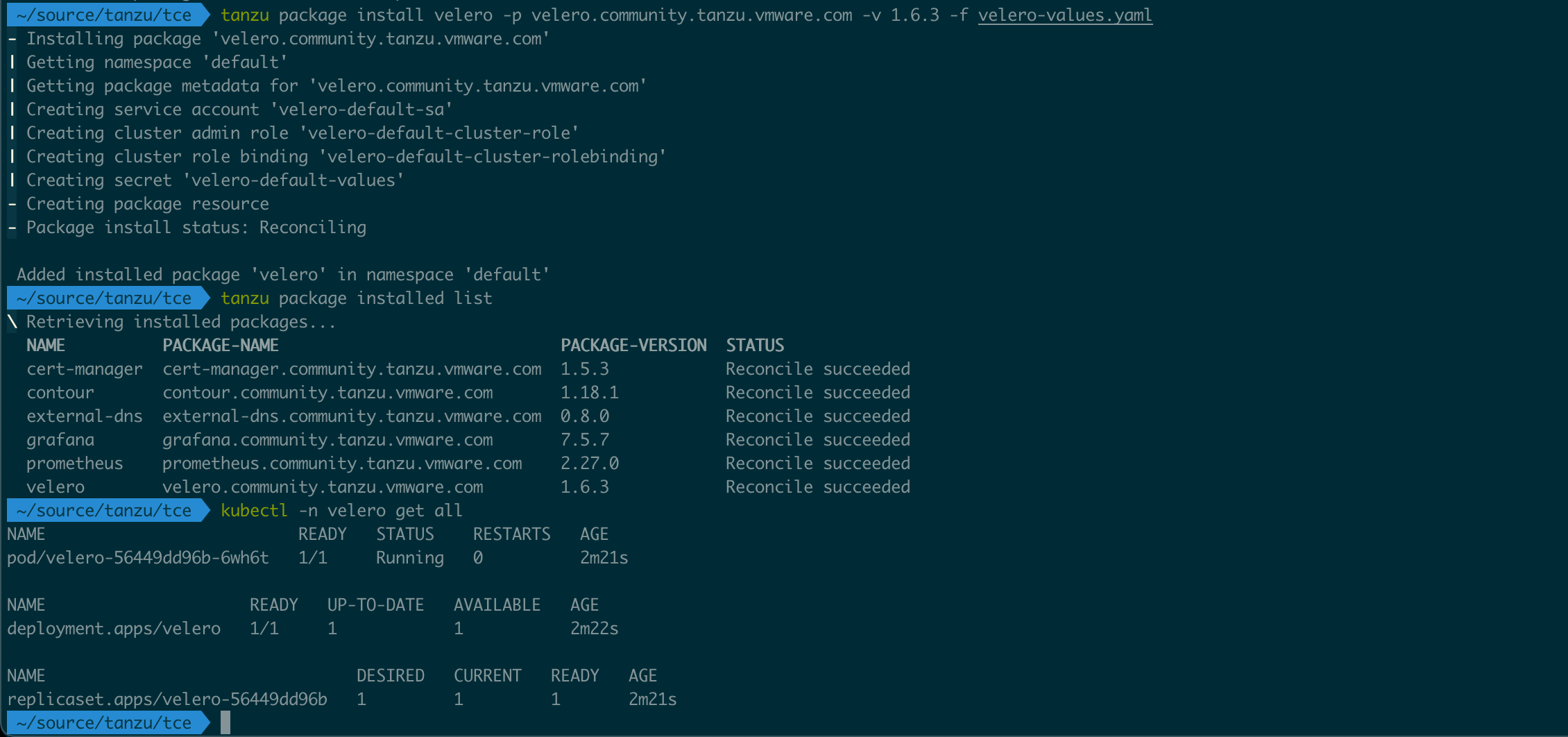
Test backup
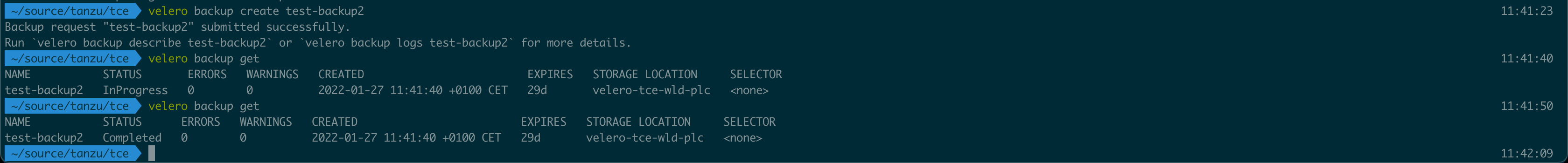
With Velero deployed we can verify that it works with the Velero CLI
I'm using a VMware provided velero cli package referenced here
1velero backup create <backup-name>
2
3velero backup get
With Velero we can use different selectors for filtering what to backup, refer to the documentation for more info. Let's see an example of how to create a backup of a namespace
1velero backup create <backup-name> --include-namespaces <namespace>
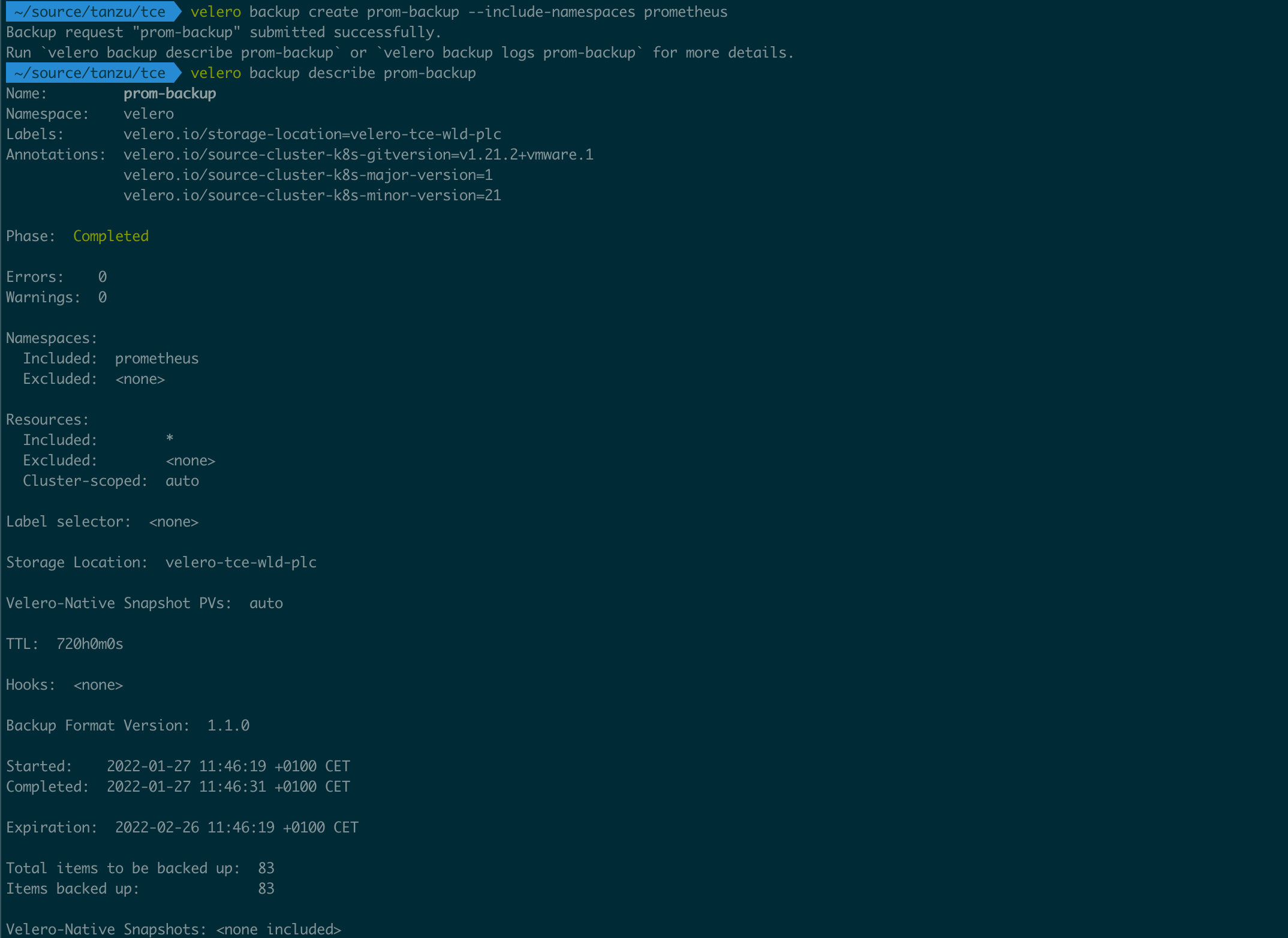
Verify backup target
Now, let's check out our object storage target to see what we have
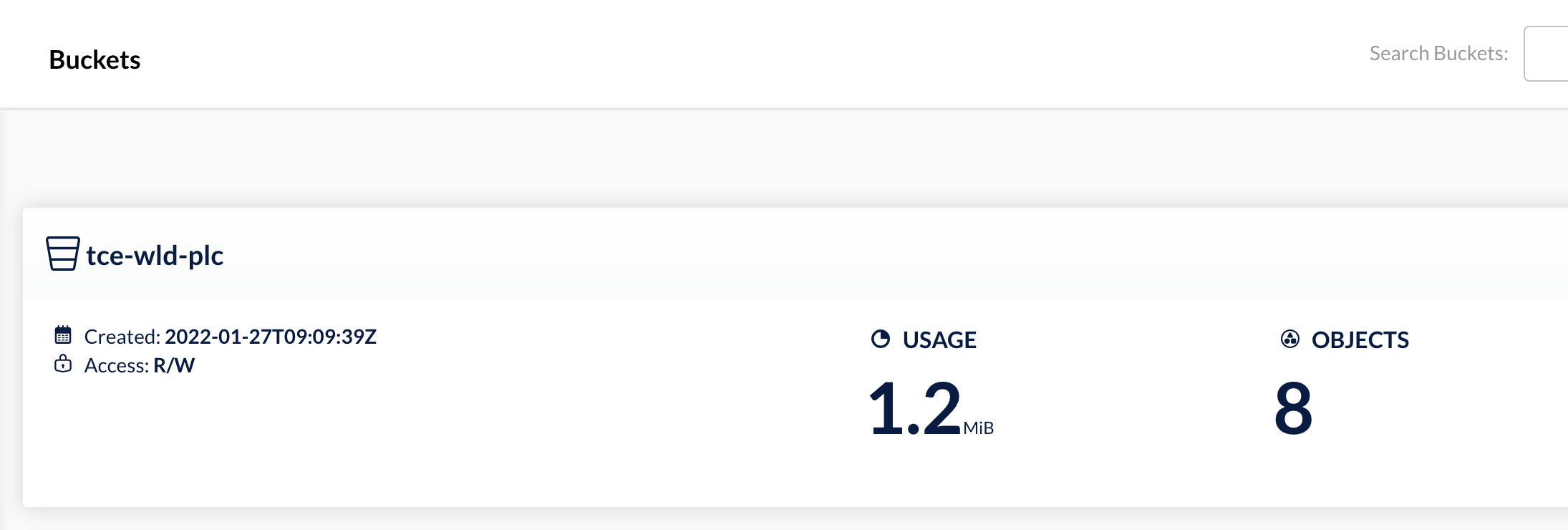
If we navigate in to the bucket we can see we have got a backups folder and inside of that we have folders for the two backups we created
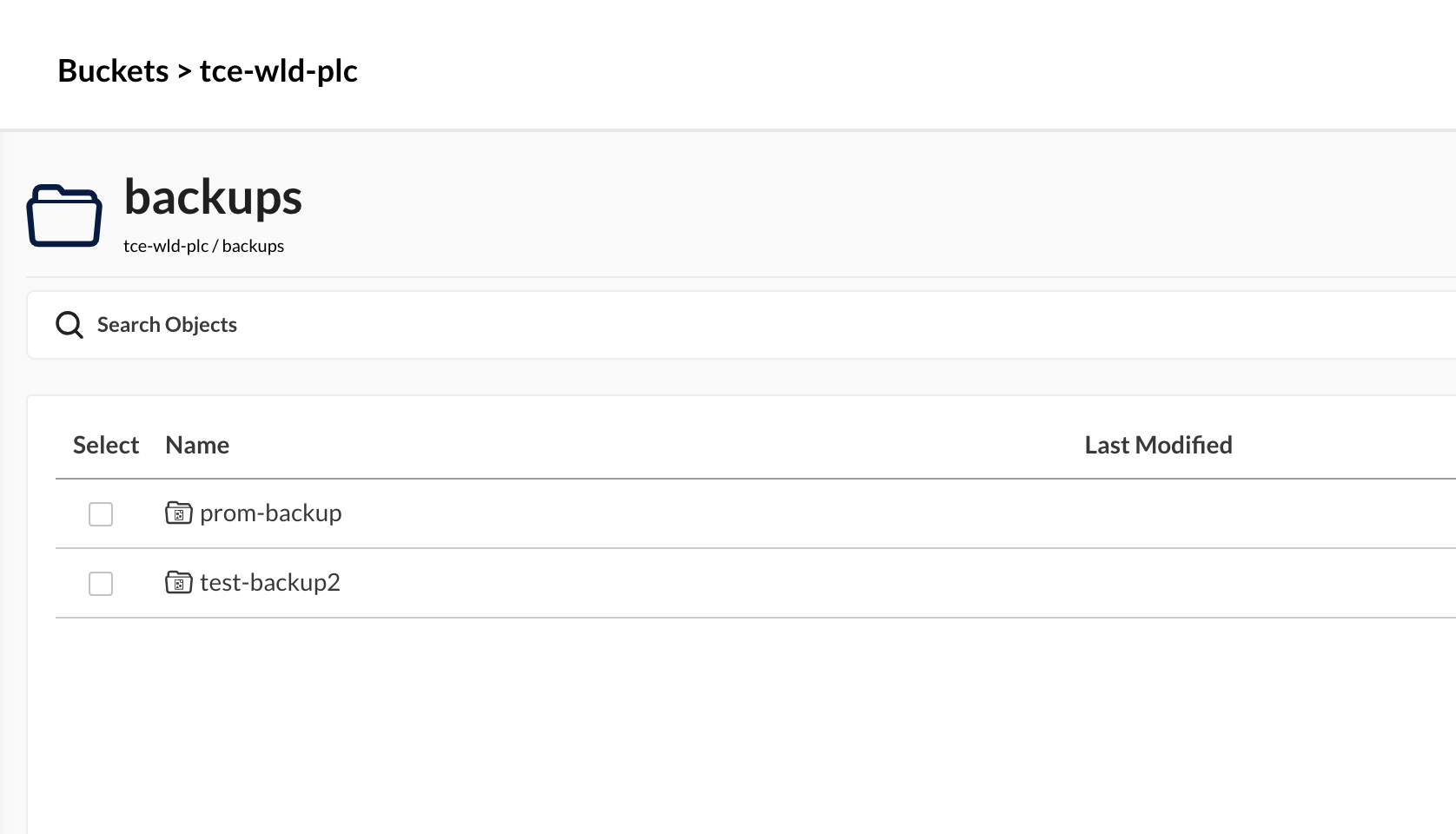
For a few examples on restore please check out my previous post
Summary
This post has been a quick intro on how to get Velero up and running on a TCE cluster. As mentioned a few times already I have this post discussing a few more examples, and also how to set up a local MinIO object storage server
Please feel free to reach out if you have any questions or comments