CKA Study notes - Resource Requirements and limits
This post is part of my Certified Kubernetes Administrator exam preparations. Now we'll take a look at how to specify the resource requirements and limits we can set on a container in a Pod
With requirements we can specify how much resources a container needs, and with limits we can specify the maximum of resources a Pod can use
Note #1: I'm using documentation for version 1.19 in my references below as this is the version used in the current (jan 2021) CKA exam. Please check the version applicable to your usecase and/or environment
Note #2: This is a post covering my study notes preparing for the CKA exam and reflects my understanding of the topic, and what I have focused on during my preparations.
Resource Types
Kubernetes Documentation reference
First let's take a look at what resources we can request and limit.
Currently the types available are Compute resources, meaning cpu and memory.
CPU
CPU are specified in units of Kubernetes CPUs where one CPU in Kubernetes is equal to 1 core or vCPU.
Oftentimes we see resource specificying CPU in a fraction of this, e.g. 500m or 0.5. The smallest amount that can be requested are 1m, e.g. a milli CPU (1/1000 CPU core). 500m (or 0.5) is equal to 500 millicpus, e.g. 500/1000 CPU, in short half a CPU (core).
Memory
Memory is specified in bytes and not different from working with memory in "normal" environments.
Memory can be expressed as a plain integer or with one of the suffixes, K, M, G, T, P or E. We can also use the "power-of-two" equivalents, Ki, Mi, Gi, Ti, Pi or Ei.
Specifying request and limit
The request and limit specification is done in the resources section of a container spec.
Let's see an example
1apiVersion: v1
2kind: Pod
3metadata:
4 name: <pod-name>
5spec:
6 containers:
7 - name: <container-name>
8 image: <image>
9 resources:
10 requests:
11 cpu: 100m
12 memory: 250Mi
13 limits:
14 cpu: 250m
15 memory: 500Mi
If we take a look at the Pod description we can see that our resource requests and limits are specified
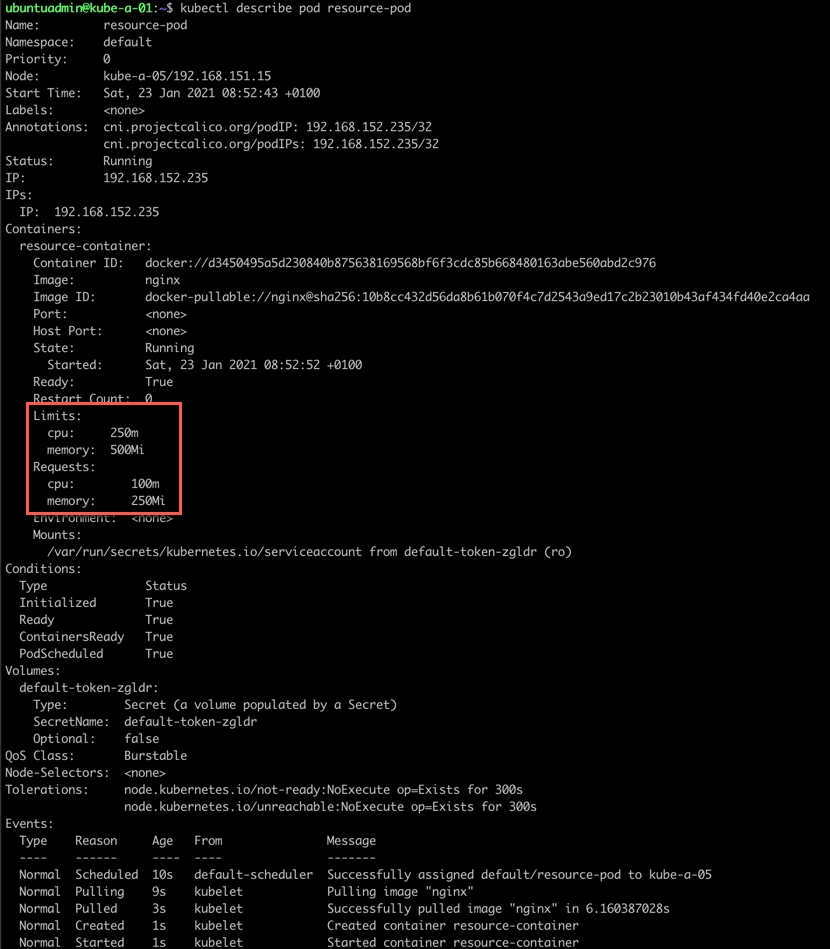
In this example the container inside this Pod will be assigned a minimum of 0.1 CPU and 250 Mebibytes of memory. If it needs the resources it can have a maximum of 0.25 (a quarter) of a CPU and 500 Mebibytes of memory.
Pod scheduling with resources
The Kubernetes scheduler will take the resource specification of a pod into account when scheduling and running the pod. The scheduler will ensure that the total amount of requested resources for all containers in all pods on that node can be met.
How the resources are specified for a container and what happens if it exceeds can be dependant on the container runtime used.
For instance for Docker the CPU request will be specified through the --cpu-shares parameter whereas the memory limit is used for the --memory parameter.
CPU are often measured or permitted inside a specific quota period, normally this is 100ms. The kubelet will determine this by multipling the fractional CPU limit (for example 100m) with the quota period (for example 100) and this is how much the CPU can use inside the quota period.
If a container exceeds it memory limit it might be terminated or restarted based on the container specification
Take a look at the Kubernetes documentation for more reference on how containers are run with requests and limits.
Monitoring
Kubernetes Documentation reference
The used resources is reported in the Pod status.
Oftentimes we will have installed more specific tools for monitoring in a Kubernetes cluster through the Metrics API.
Summary
This post has been an introduction to specifying resources and limits for containers. For the CKA/D exams I think it's sufficient to know how to specify it, possibly we need to spot this as a possible failure cause when troubleshooting.
For more info and a few examples that can help with the understanding of this topic, check these two articles: